Agriculture Optional Syllabus for UPSC Mains – A Complete Breakdown
Agriculture is one of the popular optional subjects in UPSC Civil Services Examination due to its scoring potential and relevance to topics in GS Papers and Essay writing. The syllabus is well-defined and covers both theoretical and practical aspects of agricultural science.
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
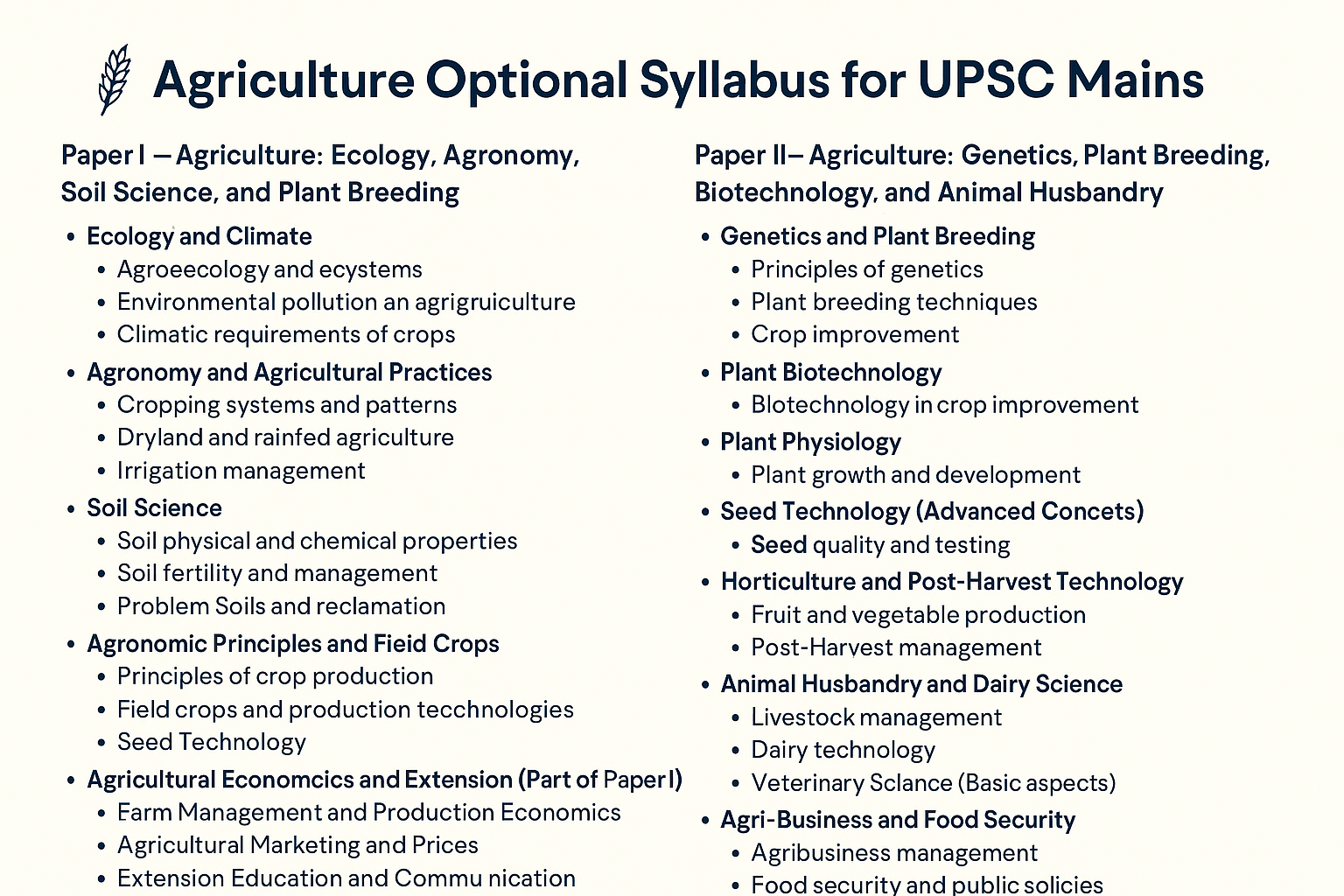
Paper I – Agriculture: Ecology, Agronomy, Soil Science, and Plant Breeding
Paper I is more foundational and scientific, covering ecology, agronomy, soil sciences, and crop production principles. Here’s a detailed topic-wise breakdown:
1. Ecology and Climate
- Agroecology and Ecosystems
- Concepts of ecosystems and agro-ecosystems
- Energy flow, nutrient cycling, and ecological balance
- Sustainable agriculture: ecological principles and their practical implications
- Environmental Pollution and Agriculture
- Air, water, soil pollution and their effects on crops and livestock
- Climate change, global warming and its impact on agriculture
- Conservation agriculture and climate-resilient agriculture
- Climatic Requirements of Crops
- Elements of climate and weather
- Influence of weather on crop growth and productivity
- Agro-climatic zones of India – classification and significance
2. Agronomy and Agricultural Practices
- Cropping Systems and Patterns
- Mono-cropping, multiple cropping, relay cropping, intercropping
- Cropping intensity and productivity enhancement
- Dryland and Rainfed Agriculture
- Challenges and techniques for moisture conservation
- Drought resistance in crops
- Watershed management and water harvesting
- Irrigation Management
- Types of irrigation systems: surface, sub-surface, drip, sprinkler
- Irrigation scheduling and efficiency
- Water-use efficiency and deficit irrigation
- Weed Science
- Classification, biology, and ecology of weeds
- Integrated weed management: cultural, mechanical, biological, and chemical methods
To Enroll in FIRST IAS INSTITUTE - Click Here
3. Soil Science
- Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
- Soil texture, structure, water, air, temperature
- pH, salinity, sodicity, and nutrient status
- Soil Fertility and Management
- Nutrient cycles (NPK)
- Organic matter, composting, vermicomposting
- Biofertilizers, green manuring
- Problem Soils and Reclamation
- Saline, alkaline, acidic soils
- Reclamation methods and soil amendments
4. Agronomic Principles and Field Crops
- Principles of Crop Production
- Growth and development of crops
- Yield attributes and physiological maturity
- Factors affecting crop productivity
- Field Crops and Production Technologies
- Cereals: Rice, Wheat, Maize, Barley
- Pulses: Gram, Arhar, Lentil
- Oilseeds: Groundnut, Mustard, Soybean, Sunflower
- Commercial crops: Sugarcane, Cotton, Jute, Tobacco
- Seed Technology
- Seed production, certification, testing, and storage
- Hybrid seed production and GM crops
5. Agricultural Economics and Extension (Part of Paper I)
- Farm Management and Production Economics
- Cost concepts and farm budgeting
- Risk and uncertainty in agriculture
- Agricultural Marketing and Prices
- Marketing channels, price spread
- Minimum Support Prices (MSP), buffer stock, PDS
- WTO and Indian agriculture
- Extension Education and Communication
- Methods of communication in rural areas
- Agricultural extension programs: KVKs, ATMA, and T&V System.
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
Paper II – Agriculture: Genetics, Plant Breeding, Biotechnology, and Animal Husbandry
Paper II delves into applied sciences such as plant breeding, genetics, biotechnology, and animal husbandry.
1. Genetics and Plant Breeding
- Principles of Genetics
- Mendelian inheritance, chromosome structure and function
- Gene expression and mutation
- Population genetics and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
- Plant Breeding Techniques
- Methods: Selection, hybridization, backcrossing, mutation breeding
- Heterosis and inbreeding depression
- Breeding for biotic and abiotic stress resistance
- Crop Improvement
- Genetic resources and germplasm conservation
- Varietal development and release
- Role of ICAR and IARI in crop improvement
2. Plant Biotechnology
- Biotechnology in Crop Improvement
- Genetic engineering, transgenic crops
- Tissue culture: micropropagation, somaclonal variation
- Molecular markers and MAS (Marker Assisted Selection)
- Bioinformatics and Genomics
- Use of bioinformatics in plant breeding
- Genome sequencing, CRISPR-Cas9 and gene editing
3. Plant Physiology
- Plant Growth and Development
- Photosynthesis, respiration, transpiration
- Plant growth regulators: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ABA, ethylene
- Physiological Disorders and Stress Physiology
- Water stress, salinity, temperature extremes
- Mechanisms of stress tolerance
4. Seed Technology (Advanced Concepts)
- Seed Quality and Testing
- Seed vigor, viability, and purity standards
- ISTA rules and procedures
- Seed Certification and Regulation
- Seed Act and related policies
- Intellectual Property Rights and plant varieties protection
To Enroll in FIRST IAS INSTITUTE - Click Here
5. Horticulture and Post-Harvest Technology
- Fruit and Vegetable Production
- Propagation techniques, orchard management
- Protected cultivation and integrated farming systems
- Post-Harvest Management
- Storage, preservation, value addition
- Cold chain infrastructure and marketing
6. Animal Husbandry and Dairy Science
- Livestock Management
- Breeds of cattle, buffalo, goat, sheep, and poultry
- Housing, feeding, breeding, and health care
- Dairy Technology
- Milk processing, pasteurization, preservation techniques
- Fodder crops and feed formulation
- Veterinary Science (Basic Aspects)
- Common animal diseases and control measures
- Role of livestock in rural economy
7. Agricultural Microbiology
- Soil and Rhizosphere Microorganisms
- Nitrogen fixation, mycorrhizae, decomposers
- Bio-pesticides and bio-control agents
- Microbial Biotechnology
- Fermentation, bio-fertilizers, enzyme production
8. Agri-Business and Food Security
- Agribusiness Management
- Agri-inputs, rural entrepreneurship
- Role of start-ups and digital technology in agriculture
- Food Security and Public Policies
- Food security challenges in India
- Government schemes: NFSA, PM-KISAN, PMFBY
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
Conclusion
The UPSC Agriculture Optional syllabus is a balanced blend of scientific knowledge, practical applications, and policy aspects. It offers a great advantage to students from agricultural and life science backgrounds, but even non-agriculture graduates can master it with a good strategy and focused preparation.
Pro Tip: Supplement your preparation with ICAR textbooks, Yojana & Kurukshetra magazines, and government reports for current relevance.
 firstiasofficial@gmail.com
firstiasofficial@gmail.com
Leave a Comment