UPSC Civil Engineering Optional Syllabus for Mains
The Civil Engineering optional for UPSC is a highly technical subject suitable for candidates with a strong academic background in the field. It consists of two papers (Paper I and Paper II), each carrying 250 marks, totaling 500 marks. Below is a detailed breakdown:
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
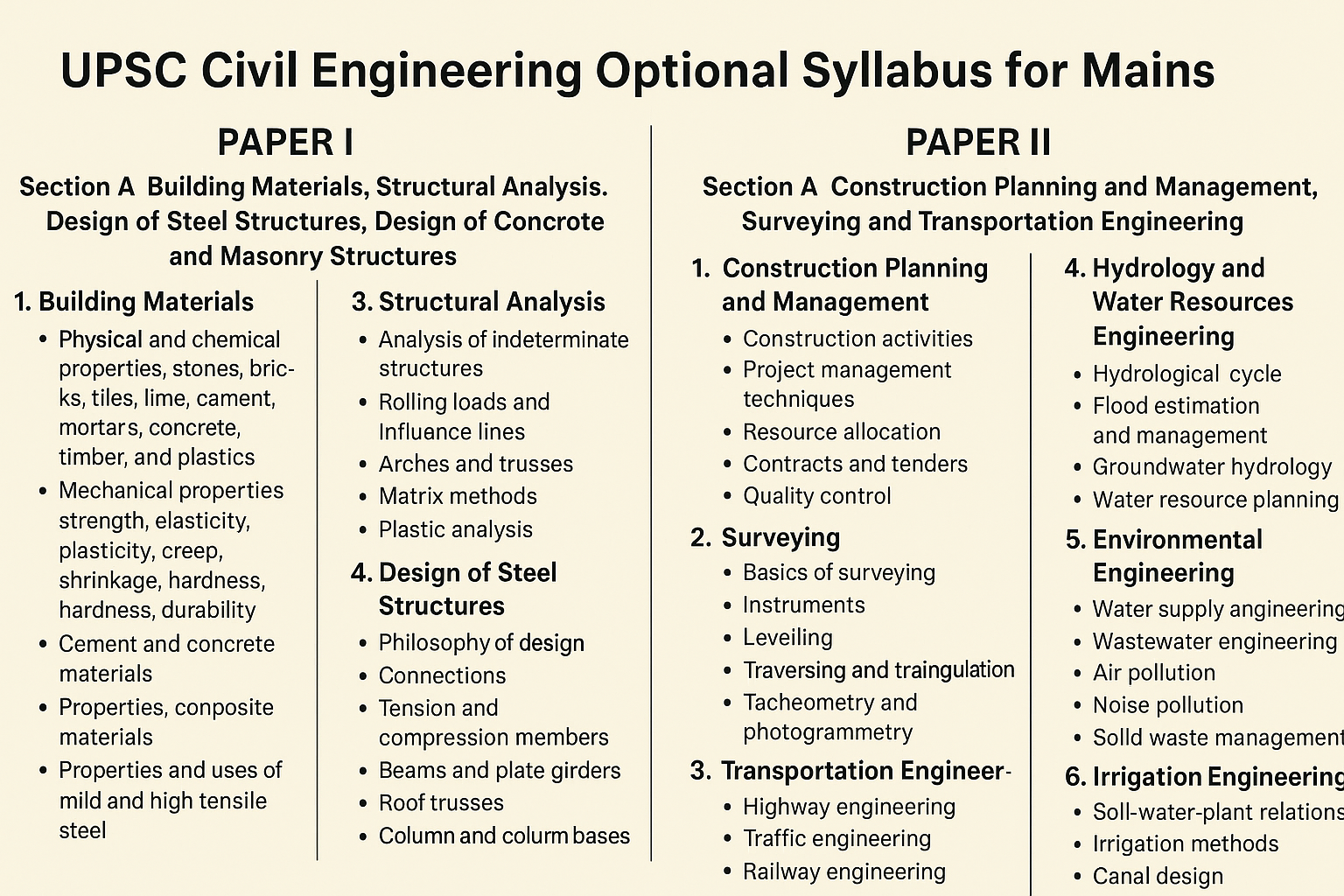
PAPER I
Section A – Building Materials, Structural Analysis, Design of Steel Structures, Design of Concrete and Masonry Structures
1. Building Materials
- Physical and Chemical Properties:
- Stones, Bricks, Tiles, Lime, Cement, Mortars, Concrete, Timber, and Plastics.
- Mechanical Properties:
- Strength, Elasticity, Plasticity, Creep, Shrinkage, Hardness, Durability.
- Cement & Concrete:
- Types of cement and their properties.
- Ingredients and mix proportions of concrete.
- Water-cement ratio.
- Workability, durability, curing methods.
- Special concretes: lightweight concrete, high-strength concrete, polymer concrete.
- Timber:
- Defects, seasoning, preservation techniques.
- Plastics & Composite Materials:
- Types, properties, applications in construction.
- Steel:
- Properties of mild steel and high tensile steel.
- Structural uses.
2. Solid Mechanics
- Stress and Strain:
- Axial, Shear, and Thermal stresses.
- Principal stresses and Mohr's circle.
- Elastic Constants:
- Poisson's ratio, Modulus of Elasticity, Bulk modulus, and Shear modulus.
- Torsion:
- Torsion of circular shafts, transmission of power, combined bending and torsion.
- Bending:
- Theory of simple bending, bending stress distribution, shear stress in beams.
- Deflection:
- Deflection of beams and cantilevers using various methods (double integration, moment area).
- Columns:
- Euler’s theory, Rankine’s formula, buckling.
3. Structural Analysis
- Analysis of Indeterminate Structures:
- Methods: Moment distribution, Slope deflection, Kani’s method, Castigliano’s theorem.
- Rolling Loads & Influence Lines:
- Influence line diagrams for simply supported beams, maximum shear force and bending moment.
- Arches & Trusses:
- Three-hinged and two-hinged arches.
- Analysis of perfect frames using graphical and analytical methods.
- Matrix Methods:
- Flexibility and stiffness method basics.
- Plastic Analysis:
- Concept of plastic hinge, collapse load.
4. Design of Steel Structures
- Philosophy of Design:
- Limit state method, Working stress method.
- Connections:
- Riveted, bolted, and welded joints.
- Tension and Compression Members:
- Design of struts and ties.
- Beams and Plate Girders:
- Laterally supported and unsupported beams.
- Web buckling, web crippling.
- Roof Trusses:
- Design of purlins and joints.
- Column and Column Bases:
- Design of columns under axial and biaxial bending.
- Industrial Structures:
- Gantry girders and industrial frame analysis.
5. Design of Concrete and Masonry Structures
- Working Stress and Limit State Method:
- Comparison and applicability.
- Reinforced Concrete Elements:
- Design of singly and doubly reinforced beams.
- T-beams, one-way and two-way slabs, columns, footings.
- Prestressed Concrete:
- Principles, losses in prestress, design of simple members.
- Water Retaining Structures:
- Underground and overhead tanks, design criteria.
- Masonry Structures:
- Design of load-bearing walls, reinforced masonry.
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
PAPER II
Section A – Construction Planning and Management, Surveying and Transportation Engineering
1. Construction Planning and Management
- Construction Activities:
- Types and methods, construction equipment.
- Project Management Techniques:
- PERT and CPM, network analysis.
- Time-cost optimization.
- Resource Allocation:
- Labor, materials, equipment planning.
- Contracts and Tenders:
- Types, conditions, dispute resolution, arbitration.
- Quality Control:
- Statistical quality control, ISO standards.
2. Surveying
- Basics of Surveying:
- Principles, errors, classifications.
- Instruments:
- Theodolite, EDM, total station, auto level.
- Levelling:
- Differential levelling, contouring.
- Traversing and Triangulation:
- Methods, adjustments, applications.
- Tacheometry and Photogrammetry:
- Field applications and computations.
- Remote Sensing and GIS:
- Concepts and applications in civil engineering.
3. Transportation Engineering
- Highway Engineering:
- Geometric design, cross-section, horizontal and vertical alignment.
- Design of flexible and rigid pavements.
- Traffic Engineering:
- Traffic surveys, speed, volume, accidents.
- Traffic signals, road signs, and markings.
- Railway Engineering:
- Permanent way components, gauges, track layouts.
- Points and crossings, station yards.
- Airport Engineering:
- Runway and taxiway design, zoning laws.
- Harbor Engineering:
- Port layout, breakwaters, jetties, berthing areas.
Section B – Hydrology, Water Resources, Environmental Engineering, and Irrigation Engineering
4. Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering
- Hydrological Cycle:
- Precipitation, evaporation, infiltration, runoff.
- Flood Estimation and Management:
- Design floods, hydrographs, reservoir routing.
- Groundwater Hydrology:
- Aquifer properties, well hydraulics.
- Water Resource Planning:
- Multipurpose projects, reservoir planning.
5. Environmental Engineering
- Water Supply Engineering:
- Source, intake, treatment, and distribution of water.
- Wastewater Engineering:
- Sewerage systems, sewage treatment methods.
- Air Pollution:
- Causes, effects, control methods.
- Noise Pollution:
- Sources, measurement, control.
- Solid Waste Management:
- Collection, transport, disposal, recycling.
6. Irrigation Engineering
- Soil-Water-Plant Relationship:
- Consumptive use, crop water requirement.
- Irrigation Methods:
- Surface, sprinkler, drip.
- Canal Design:
- Kennedy’s and Lacey’s theories.
- Water Logging and Drainage:
- Causes, effects, control measures.
- Dams and Spillways:
- Classification, design of gravity and earth dams.
- Types and design of spillways.
- Cross Drainage Works:
- Aqueducts, syphon aqueducts, superpassage.
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
Conclusion
The Civil Engineering optional offers a technical and scoring edge for aspirants with a core engineering background. A well-structured study plan focusing on both theoretical concepts and practical applications, supported by diagrams, derivations, and design examples, is key to scoring well in this optional.
 firstiasofficial@gmail.com
firstiasofficial@gmail.com
Leave a Comment