UPSC Botany Optional Syllabus for Mains: A Comprehensive Guide
The Botany Optional in the UPSC Civil Services Mains Examination is a popular choice among aspirants with a background in life sciences, agriculture, or biotechnology. The syllabus is divided into two papers — Paper I and Paper II — each carrying 250 marks, making it a total of 500 marks. Here's a detailed breakdown of the latest syllabus as per the UPSC notification, along with key subtopics and descriptions.
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
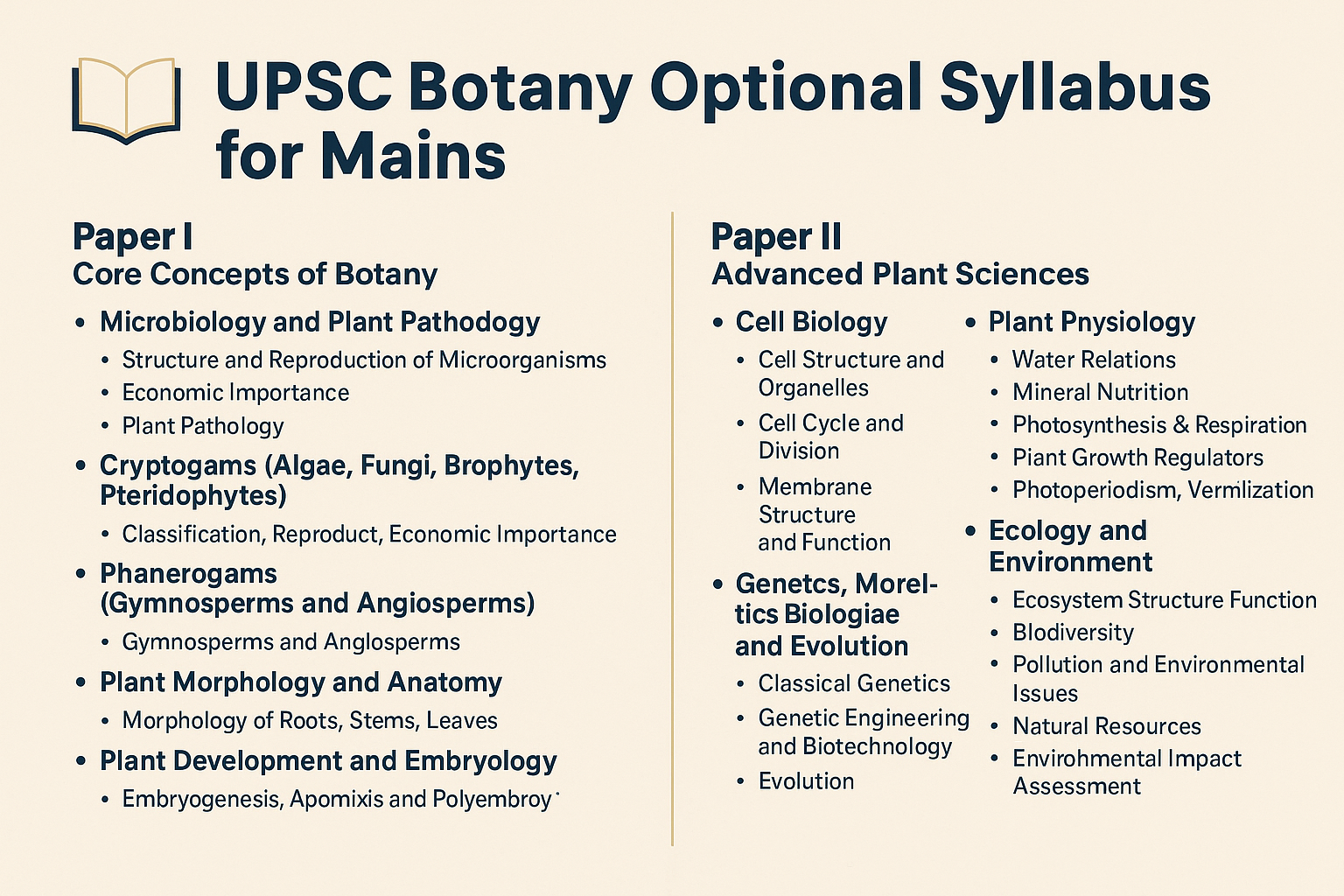
Paper I – Core Concepts of Botany
This paper deals with the fundamentals of plant biology, covering topics like microbiology, plant pathology, cryptogams, morphology, anatomy, and more.
1. Microbiology and Plant Pathology
- Structure and Reproduction of Microorganisms
- Bacteria: Structure, reproduction, transformation, transduction, conjugation.
- Viruses: Types (bacteriophages, plant viruses, animal viruses), replication, structure (DNA and RNA viruses).
- Mycoplasma: Characteristics and diseases.
- Economic Importance
- Role in nitrogen fixation, fermentation (yeast, lactic acid bacteria).
- Industrial applications: Antibiotics, enzymes, alcohol production.
- Plant Pathology
- Diseases caused by fungi, bacteria, and viruses.
- Symptoms, causal organisms, and control measures.
- Examples: Rust of wheat, bacterial blight of rice, mosaic disease in tobacco.
2. Cryptogams (Algae, Fungi, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes)
- Algae
- Classification, thallus organization, reproduction.
- Economic importance: Biofertilizers (e.g., blue-green algae), algae in biofuel and industry.
- Fungi
- General characteristics, reproduction (sexual and asexual), classification.
- Mycorrhizae and their ecological roles.
- Bryophytes
- Classification: Liverworts, hornworts, mosses.
- Life cycle and alternation of generations.
- Role in succession and soil formation.
- Pteridophytes
- Structural adaptations, reproduction.
- Concept of heterospory and seed habit.
- Apogamy and apospory.
To Enroll in FIRST IAS INSTITUTE - Click Here
3. Phanerogams (Gymnosperms and Angiosperms)
- Gymnosperms
- General characteristics, classification.
- Examples: Cycas, Pinus, Gnetum.
- Life cycles and economic importance.
- Angiosperms
- Classification systems: Bentham & Hooker, Engler & Prantl, APG system (modern).
- Comparative morphology and evolutionary relationships.
4. Plant Morphology and Anatomy
- Morphology
- Modifications of root, stem, leaf.
- Types of inflorescences, flowers, fruits, and seeds.
- Anatomy
- Tissues: Meristematic and permanent.
- Anatomy of dicot and monocot stems, roots, and leaves.
- Secondary growth in stems and roots.
- Anomalous secondary growth in dicots.
- Wood types and their structure.
5. Plant Development and Embryology
- Embryology
- Development of anther and pollen.
- Ovule types and development.
- Double fertilization and triple fusion.
- Endosperm formation and types.
- Embryogenesis in dicots and monocots.
- Apomixis and Polyembryony
- Mechanisms, significance in plant breeding.
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
Paper II – Advanced Plant Sciences
This paper dives into modern plant biology, including cell biology, genetics, physiology, biotechnology, and ecology, emphasizing applications and analytical aspects.
1. Cell Biology
- Cell Structure and Organelles
- Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells.
- Structure and function of organelles: Nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes.
- Cell Cycle and Division
- Mitosis and meiosis: Mechanism, significance.
- Regulation of cell cycle: Cyclins and CDKs.
- Membrane Structure and Function
- Fluid mosaic model.
- Transport mechanisms: Active, passive, facilitated diffusion, endocytosis, exocytosis.
2. Genetics, Molecular Biology and Evolution
- Classical Genetics
- Mendel’s laws, gene interactions.
- Linkage, crossing over, chromosome mapping.
- Molecular Genetics
- Structure and function of DNA and RNA.
- Replication, transcription, translation.
- Genetic code and mutations.
- Operon model (Lac Operon, Trp Operon).
- Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
- Recombinant DNA technology.
- Vectors: Plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids.
- Applications: GM crops, insulin, gene therapy.
- Genomics and proteomics.
- Evolution
- Origin of life theories.
- Darwinism, neo-Darwinism.
- Speciation, Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
To Enroll in FIRST IAS INSTITUTE - Click Here
3. Plant Breeding, Biotechnology, and Biostatistics
- Plant Breeding
- Methods: Hybridization, selection, mutation breeding.
- Breeding for disease resistance and yield.
- Biotechnology
- Tissue culture: Techniques, micropropagation, somaclonal variation.
- Applications in crop improvement, stress resistance.
- Biostatistics
- Statistical measures: Mean, median, mode, standard deviation.
- Tests: Chi-square, t-test, ANOVA.
- Significance and probability in biological experiments.
4. Plant Physiology
- Water Relations
- Diffusion, osmosis, water potential.
- Transpiration and stomatal mechanisms.
- Mineral Nutrition
- Essential elements and their functions.
- Deficiency symptoms, hydroponics.
- Photosynthesis
- Light and dark reactions, photophosphorylation.
- C3, C4, CAM pathways.
- Respiration
- Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain.
- Energy yield comparisons.
- Plant Growth Regulators
- Types: Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ABA, ethylene.
- Role in plant growth and development.
- Photoperiodism and Vernalization
- Flowering control mechanisms.
- Phytochrome system.
5. Ecology and Environment
- Ecosystem Structure
- Components: Biotic and abiotic.
- Food chains, food webs, ecological pyramids.
- Plant Communities
- Succession, stratification, dominance.
- Biodiversity
- Hotspots, conservation strategies (in-situ, ex-situ).
- Pollution and Environmental Issues
- Air, water, soil pollution.
- Climate change, deforestation, sustainable development.
- Natural Resources
- Renewable and non-renewable.
- Conservation strategies.
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)
- Tools and techniques, significance in planning.
Join WhatsApp community for Free Notifications, Updates, Study Material, Mock Tests, Internship Updates, and Current Affairs - CLICK HERE TO JOIN
Final Thoughts
The Botany Optional syllabus for UPSC Mains demands a deep conceptual understanding as well as the ability to present answers analytically with examples, diagrams, and real-life applications. For aspirants with a science background, this optional offers a scoring advantage, especially when preparation is integrated with diagrammatic clarity and recent developments (like GMOs or climate-responsive agriculture).
 firstiasofficial@gmail.com
firstiasofficial@gmail.com
Leave a Comment